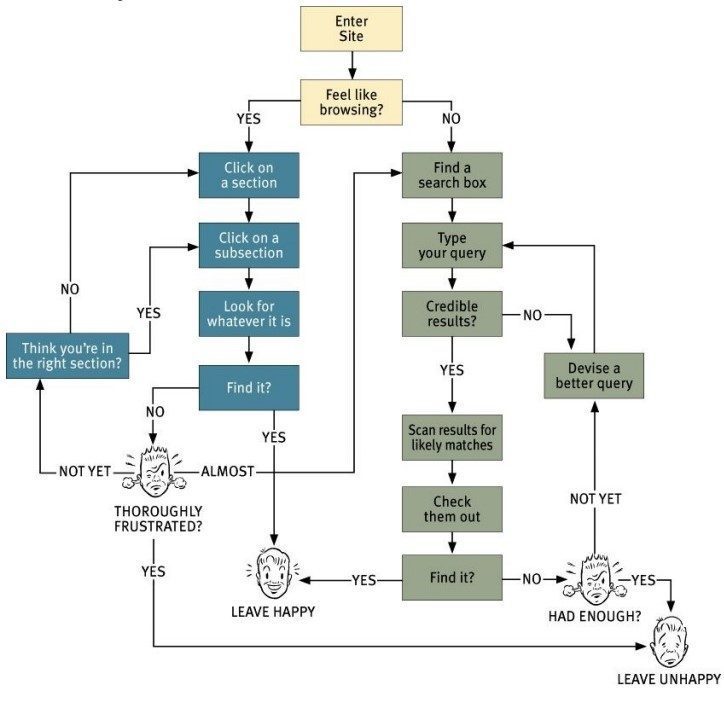
The navigation system of a website is like the road map that directs users to all the different areas and information contained in it. When the navigation system is clear and well-structured it helps to create trust and credibility, allowing visitors to easily find the information and content they are looking for. However, when that navigation system is confusing and hard to follow it will result in frustrated visitors.
When users navigate in a website, they usually have three main questions to ask:
- ‘Where am I?’,
- ‘Where have I been?’ and
- ‘Where else can I go in this site?’
As a result, and to create easy and enjoyable navigation systems, designers need to follow these suggestions:
What are the attributes of a usable navigation system?
- Have persistent navigation– a set of navigation icons displayed on each page. Persistent navigation should include these five elements:
- The Site ID (logo) – must be placed on the top left
- A search box placed on the top right
- A home button or tab
- Utilities(shopping cart, site map, help page etc.)
- Sections
There is an exception with the homepage (often it doesn’t need the persistent navigation because it is not like other pages). Also, some forms pages like the checkout page in an e-commerce website don’t need persistent navigation.
- Display a “You are here” indicator. Designers need to highlight, where the user’s current location is in navigation bars, menus or lists in the page.
- Each page must have a page name. The tab that identifies the page name needs to display the content that is unique to this specific page. Also, it needs to be outstanding (it should say, “this is the heading for the entire page”). Moreover, the name needs to match what the user clicked.
- Display Breadcrumbs. They are like a secondary navigation scheme that helps users to determine where they are; and an alternative way to navigate around a website They need to place them at the top of the site, organized in a hierarchical manner.
- Use tabs. Tabs allow users to easily access different areas of a site or different parts of an individual page. They help to group content, connect related information, and as a tool to save space in a website.
Finally, the importance of a well structured usable navigation system is critical when it comes to differentiate a brand as it plays an essential role in encouraging visitors to stay, view the web content or buy a product.