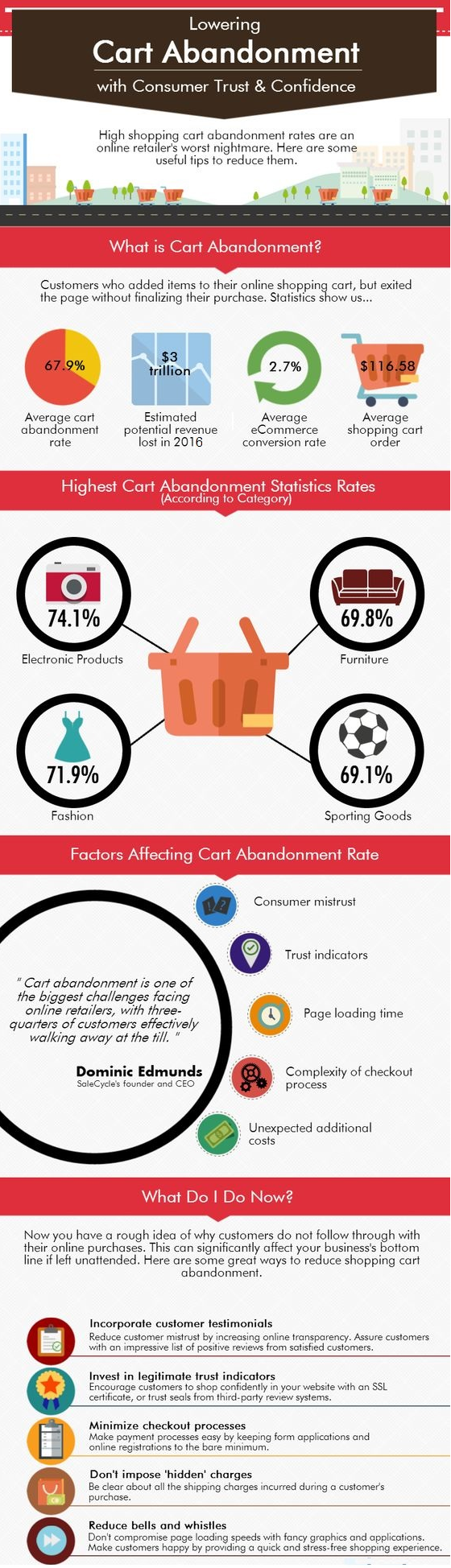
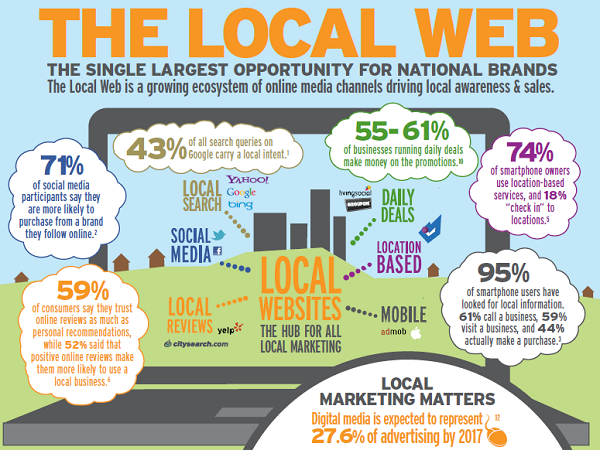
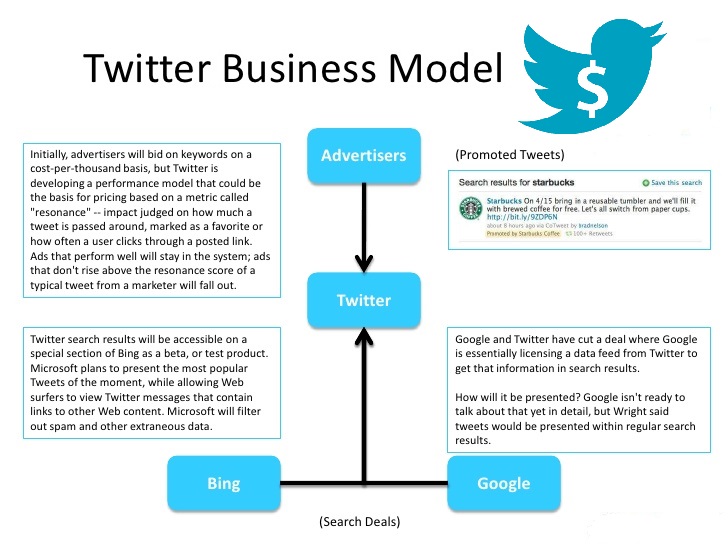
The concept of community has been defined as a group of persons that build through different signs or actions a sense of identity and belonging to such group. This definition has taken new connotations since the emergence of the web 2.0 and the rise of virtual communities.
Within the fabric of meanings that describe virtual communities, the “online brand communities”, have spawned great interest among product engineers and marketing professionals as the interaction generated in such spaces have become significant sources of market intelligence.
Some theoretical principles of digital anthropology, suggest that if a group of consumers admire and follow a brand in a virtual community, a process of class consciousness is developed through multiple rituals that reproduce the sense of belonging to the community and foster the affective bonds among members and the brand.
For some companies, learning about online brand communities’ rituals and traditions has been crucial in order to gather key customers’ behavior information. Moreover, such learning approaches have helped companies to exploit the affective bonds that connect community members with the brand, generating dynamics of active participation with mutual benefits for both parties.
How can brands interact in online brand communities to design products?
A successful business case of active participation happened between the Danish manufacturer of plastic toys, Lego Corp. and the followers of the brand who interact in the online community; Lugnet (www.lugnet.biz). The interaction between Lugnet and LEGO Corp. is determined by LEGO’s necessity to know what kind of products Lugnet members would like the company to produce and buy.
In order to capitalize the interactions created with Lugnet, LEGO corp. designed a strategy aimed to encourage Lugnet members to participate in a contest to design different products that they would like LEGO corp. to produce.
During the contest, LEGO provided a software of prototypes to the community so members could design a specific product online and share the design with other members. Once the leaders of Lugnet in partnership with the engineering department of LEGO Corp. choose the winning model, the company developed the product, rewarding the most active members in the contest.
LEGO strategy of empowering Lugnet members to take part of its product design process was beneficial for both parts: On the one hand, LEGO benefited from gathering key business information that improves product sales and customer satisfaction. On the other hand, Lugnet members buy products designed by themselves while reinforcing the affective ties with the brand and with other community members.