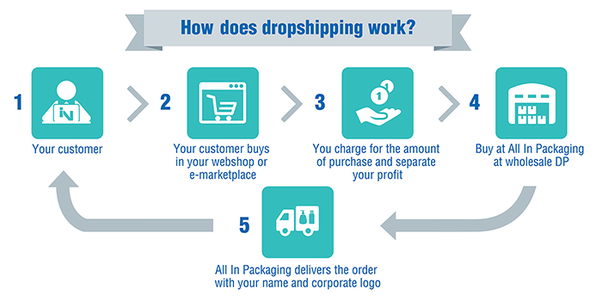
Since the inception of e-commerce as a new way for entrepreneurs and customers to participate in online marketplaces, drop shipping became one of the most popular methods used by consumers to make their purchases.
Drop shipping is defined as a retail fulfillment method in which a merchant sells products without having a physical store or keeping a large inventory but still getting a wholesale price from a supplier. Moreover, when the merchant sells a product, it purchases the item from a third party and ship it directly to the customer.
Although this online business model has been expanding exponentially in the last few years, there are some benefits and disadvantages entrepreneurs need to consider before starting a drop shipping business.
Benefits:
- Low financial risks: Usually the drop shipping business model offers an inexpensive manner to procure inventory which is not possible otherwise. This makes it less risky than investing large amounts of money on acquiring inventory.
- Fast Profitability: If the drop shipping business model is executed following an insightful online marketing strategy, it will convert well, yielding at the same time immediate profits.
- Location flexibility: A drop shipping business can be operated from any location that has internet connection. Moreover, it can be run from anywhere as long as merchants can communicate with suppliers and customers.
- Wider Product Selection: In the drop shipping model, merchants do not need to pre-purchase items for sell. As a result, they can offer a wide variety of products, increasing the availability of items when suppliers stock a new item at no additional cost.
- Time and money saving: As merchants do not need to manage a warehouse, plan the shipping of products or manage stock levels, they can increase their profit margins and save management time.
Disadvantages:
- Low Entry Barriers: As merchants don’t need large amounts of capital to start the business, more people want to enter to the drop shipping business which increases competition.
- Low Margins: In the drop shipping business, most market niches are highly competitive. As a result, merchants try to drop prices in order to draw customers decreasing at the same time their revenue.
- Inventory Issues: As merchants source their products from different warehouses, inventories might change daily, making it hard to synchronize merchants store inventory with the supplier inventory.
- Supplier mistakes: Due to the large quantity of business suppliers handle, very often they make mistakes when sourcing to merchants such as missing items, wrong shipments and low-quality packing.
The drop shipping business model comes with several built-in complexities. However, a well-thought digital marketing strategy and a comprehensive business plan, can help merchants to develop a thriving, profitable drop shipping business.